The Body Zone aims to increase nutrition and physical literacy, with a goal of improving the nutritional and physical health of Ontario school children
Body Zone Apps
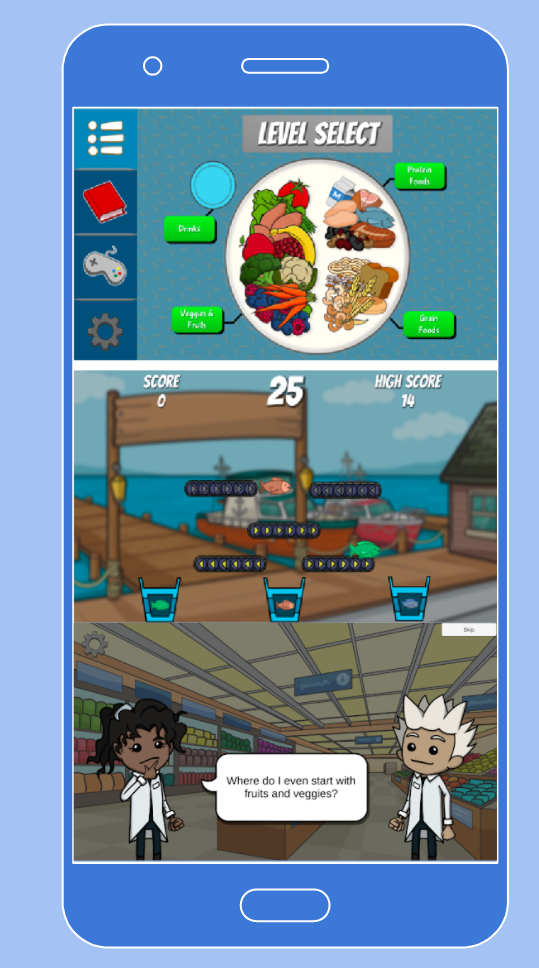
- FoodBot Factory App (Android) *mHealth app designed to teach children about food and nutrition
- FoodBot Factory App (Augmented Reality – In Development)
FoodBot Factory
FoodBot Factory is a mobile health (mHealth) app designed to teach children about food and nutrition.
The app was designed and developed by an interdisciplinary team of nutrition, education and computer science researchers.
The target population: Grade 4 and Grade 5 children (age 9-11)
The content is based on the 2019 Canada’s Food Guide,
Two versions: 2D (Android available) and an Augmented Reality (under development)
Source – Brown JM, Savaglio R, Watson G, et al. JMIR Form Res. Apr 2020;4(4):e15534.
FoodBot mHealth App Background:
Good nutrition and adequate amounts of physical activity are essential to the healthy growth and development of children.
A healthy diet in children is associated with better concentration, higher academic achievement and reduced risk of obesity. Several factors influence a child’s ability to eat healthy, including societal, environmental, social and individual-level factors. Children and adolescents today face several challenges to healthy eating. Compared to the past, they possess fewer cooking skills, which partly occurs because parents rely more on prepared foods and cook less often. Also, food skills programs have been removed from many school curriculums, despite being proven to positively influence eating habits. Environmental exposures also impact eating patterns, influence lifetime attitudes and perceptions about food, and ‘normalize’ unhealthy eating habits. This includes media advertising of unhealthy foods that is directed towards children, which is a significant concern because children rely heavily on the visual aspects of marketing and often lack the capacity to think critically about the messages communicated. Foods and meals produced for children often are of lower nutritional quality, containing higher levels of sugar, fat and salt.
Among older school children, physical activity and sports team participation are positively associated with a higher grade point average and reduced risk of obesity. Sports participation, in particular, has tremendous potential to promote positive youth development by instilling psychosocial skills that promote thriving and resilience. However, one of the contributors to both low physical activity and sports participation is physical illiteracy. Physical literacy describes the basic fundamental movement patterns (e.g., walking, running, jumping, catching) necessary to competently engage in physical activity and sports. Physical literacy proficiency in children is correlated with levels of physical activity, time spent in physical activity, and indicators of physical fitness. While some teachers are integrating daily physical activity into the classroom, children are not getting the minimum physical activity needed for the maintenance of health. All these reasons combine to make digital innovation to support healthy eating and physical activity a high-needs area.
Interventions:
The apps will directly address the need to increase nutrition and physical literacy, with a goal of improving the nutritional and physical health of Ontario school children. Content related to nutrition will include age-appropriate messages on food groups, portion sizes, healthy snacks, choosing healthy restaurants and packaged foods and reading and interpreting the Nutrition Facts table. The topic of energy balance will tie together nutrition and physical activity. Content related will also focus on increasing the physical literacy of both children and parents. The apps will also be interactive and competitive. For example, children will collect points to unlock new levels and receive badges for a certain amount of physical activity. The competitive aspect is expected to ensure adherence.